RGB vs CMYK: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to color in digital and print media, understanding the difference between RGB and CMYK color models is essential. These two systems serve different purposes and are used in different contexts, affecting how colors appear on screens and in printed materials.
What is RGB?
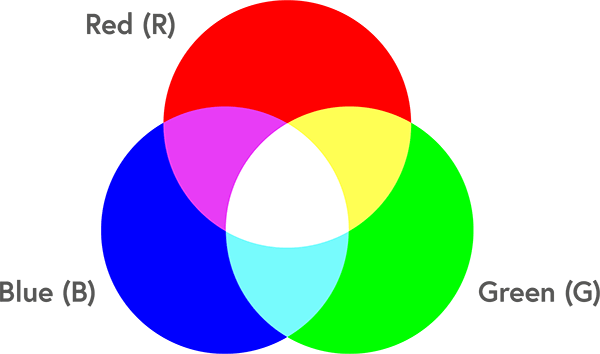
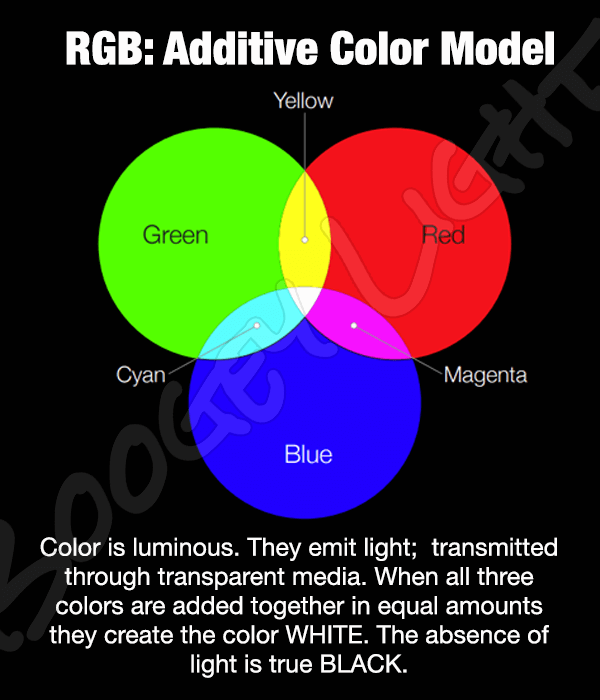
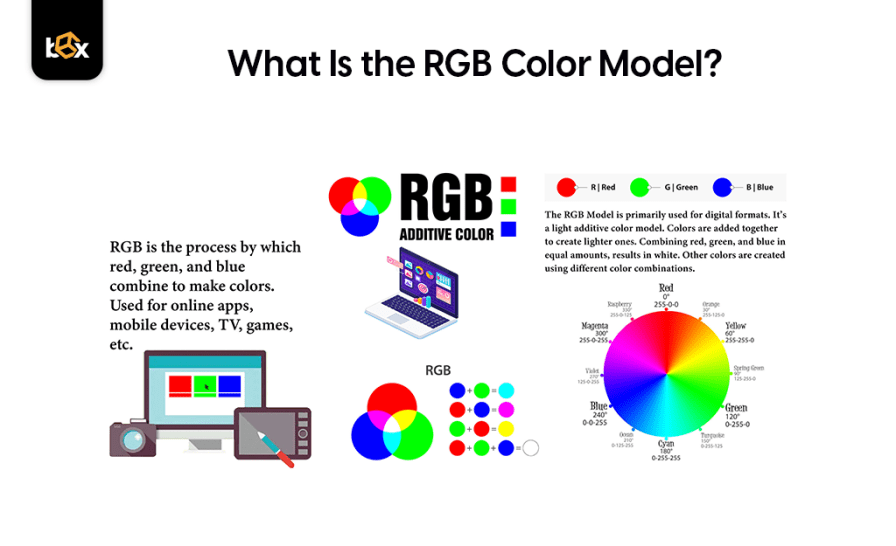
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. It is an additive color model used primarily for digital displays such as computer monitors, televisions, and smartphone screens. In this model, colors are created by combining different intensities of red, green, and blue light. When all three colors are combined at their highest intensity, they produce white light.
Key Characteristics of RGB:
- Additive Color Model: Colors are created by adding light.
- Used for Digital Displays: Ideal for screens that emit light.
- Color Range: Can produce vibrant and bright colors.
What is CMYK?
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black). It is a subtractive color model used in color printing. Unlike RGB, which uses light, CMYK works by subtracting light using ink on paper. The combination of these four inks absorbs certain wavelengths of light and reflects others, creating the perception of various colors.
Key Characteristics of CMYK:
- Subtractive Color Model: Colors are created by subtracting light.
- Used for Printing: Ideal for physical media like brochures, posters, and magazines.
- Color Range: Generally has a smaller gamut compared to RGB, meaning some colors may appear duller.
RGB vs CMYK: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | RGB | CMYK |
|---|---|---|
| Color Model | Additive | Subtractive |
| Primary Colors | Red, Green, Blue | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black |
| Usage | Digital screens | Printing |
| Color Range | Wide and vibrant | Narrower, less vibrant |
| Light Interaction | Emits light | Reflects light |
Why Does the Difference Matter?
Choosing the wrong color model can lead to unexpected results. For example, a design created in RGB might look perfect on a screen but appear dull or off-color when printed using CMYK. Understanding these differences helps designers and marketers ensure color accuracy and consistency across different media.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert RGB to CMYK?
A: Yes, but some colors in RGB cannot be perfectly replicated in CMYK due to the smaller color gamut of CMYK.
Q2: Which color model should I use for web design?
A: RGB is the standard for web and digital design because screens use light to display colors.
Q3: Is CMYK used only for printing?
A: Primarily yes, but it can also be used in some digital printing processes.
Q4: What does “Key” mean in CMYK?
A: “Key” refers to the black ink, which is used to add depth and detail to printed images.
Understanding RGB and CMYK is crucial for anyone working with colors in digital or print media. By choosing the appropriate color model, you can ensure your designs look their best no matter where they appear.